What is vitiligo?
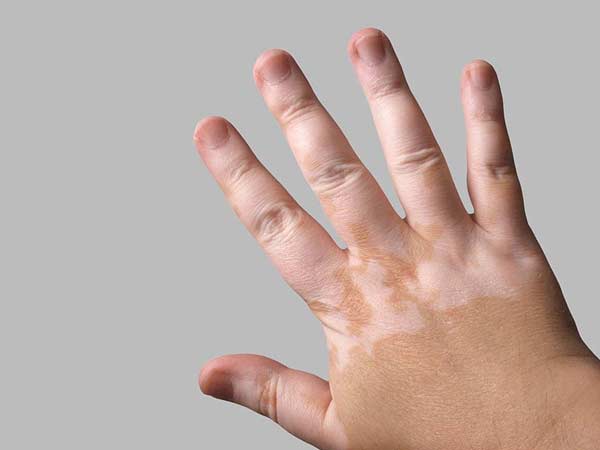
Vitiligo is a long-term skin condition in which white patches appear. It originates when there is a lack of melanin (pigment that gives color to the skin).
Vitiligo usually appears in the following areas of the body:
- Expensive
- Neck
- Hands
- Mouth (outside and inside)
- Eyes
- Fingers
- dolls
- armpits
- Groin
- Genitals
However, this condition can arise in any area of the skin.
What are the causes of vitiligo?
Vitiligo is caused by a lack of melanin in the skin. Melanin is produced in skin cells known as melanocytes, and they are what give skin its color.
Vitiligo arises because there are not enough melanocytes producing melanin in the skin. This generates the appearance of white spots on the skin or hair. There is no consensus on why the melanocytes disappear and cause vitiligo.
Some factors that can influence or trigger the appearance of vitiligo are:
- Failures in the immune system (autoimmune disease)
- Family history of vitiligo or autoimmune diseases
- Stress
- Skin damage (burns or cuts)
- Contact with certain chemicals
Is vitiligo contagious?
No, vitiligo is an internal alteration in the functioning of skin cells. It is not caused by a virus and therefore is not contagious.
Can vitiligo be prevented?
There is no way to know the exact cause of why vitiligo originates and therefore there are no methods to prevent its appearance.
Types of vitiligo
There are different types of vitiligo according to their characteristics:
- Generalized: appears in various places on the body.
- Segmented: appears on one side of the body or in a specific area.
- Mucosal: affects the mucous membranes of the mouth and/or genitals.
- Focal: it is located in a small area.
- Trichome – has a white or colorless center, an area of light pigmentation, and an area of normal colored skin.
- Universal: More than 80% of the skin on the body has no pigment.
Treatment for vitiligo
An evaluation consultation is necessary to determine the appropriate vitiligo treatment for your particular case. The consultation consists of a professional diagnosis by a dermatologist, and medical treatment, medication and home care are recommended.